General information on brain injury
Brain injury classification:
Brain injury is classified in Traumatic and Non-Traumatic:
- TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY:
Without head injury (accident, fall, heavy object on the head, blow or kick to the head, shaken baby syndrome)
With head injury (penetrating bone portion due to skull fracture, intrusion of an object such as bullet, stabbing, iron object, etc.)
- NON TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY
Infection: Bacterial or viral infections may cause:
- Encephalitis inflammation or swelling of the brain.
- Meningitis inflammation or swelling of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord.
- Brain Injury from MS
- Brain Injury from Parkinson's disease
- Brain Injury from Huntington's disease
- Brain Injury from Alzheimer's disease
Epilepsy Water Main / hydrocephalus
The brain:
Your brain is your most powerful organ, yet weighs only about three pounds. It has a texture similar to firm jelly.
The brain has three main parts.
see also our pages on consequences per brain area
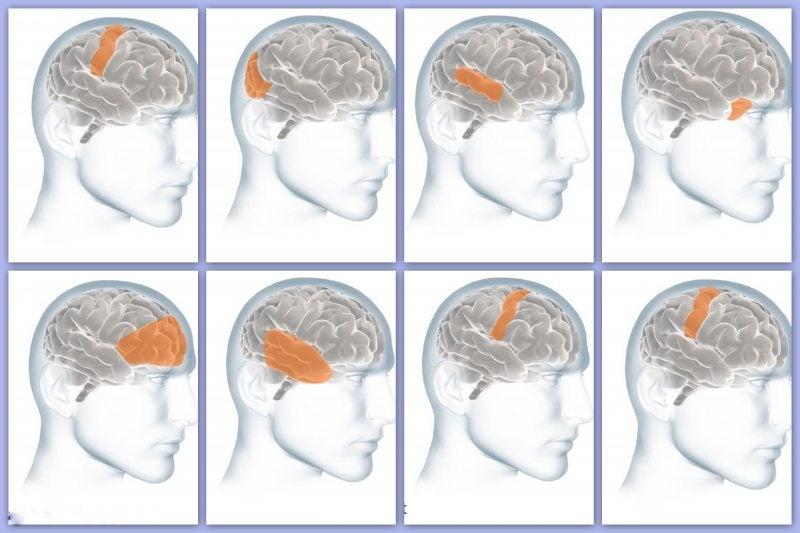
- The cerebrum fills up most of your skull. It is involved in remembering, problem solving, thinking, and feeling. It also controls movement. It is divided in two hemispheres. The right hemisphere and the left hemisphere. The picture shows the left hemisphere:

- The cerebellum (red part) is at the back of your head, under the cerebrum. It controls coordination and balance but also cognitive, linguistic and emotional functions.

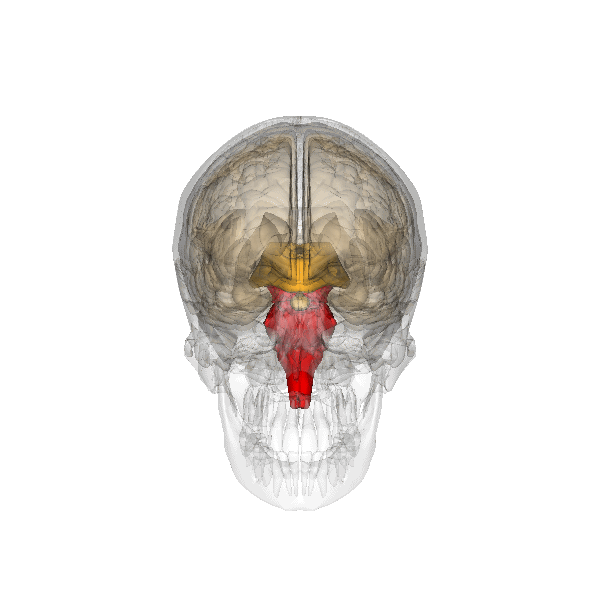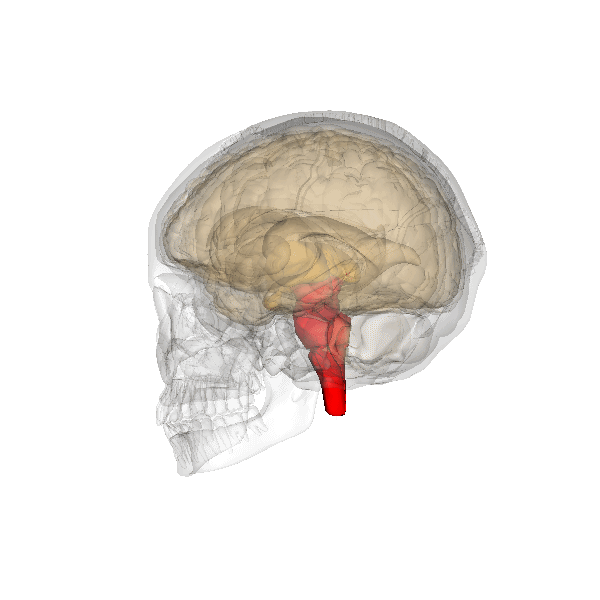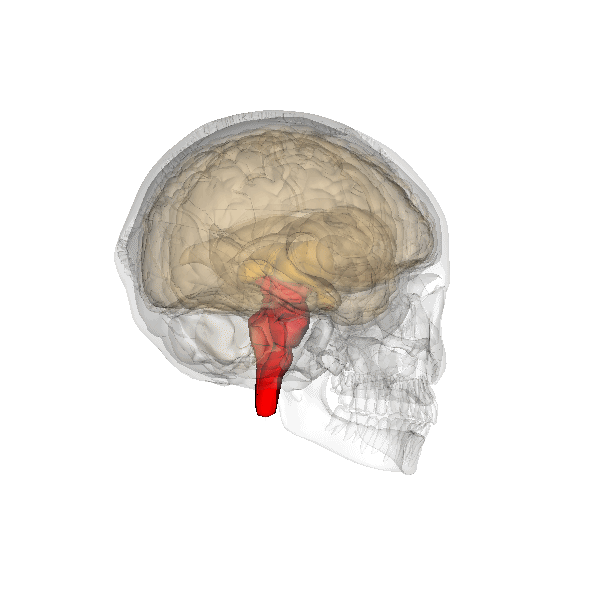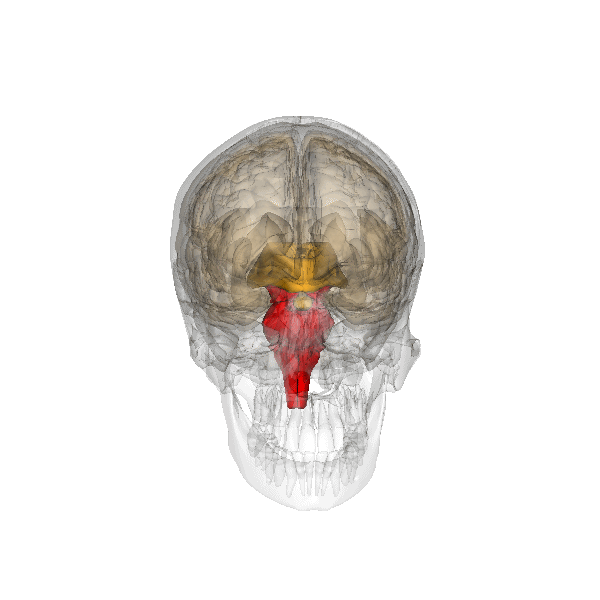
- The brain stem (red part) is beneath your cerebrum in front of your cerebellum. It consists of the medulla oblongata, the pons and the midbrain, (mesencephalon). The hypothalamus and pituitary gland belong to the brainstem also. The brainstem connects the brain to the spinal cord and controls automatic functions such as breathing, digestion, heart rate and blood pressure.
IMPACT PER BRAIN AREA:
Some forms of acquired brain injury, such as stroke or tumour, tend to cause localised damage to the brain. Others, such as hypoxia and meningitis, usually cause widespread brain damage.
The impact of acquired brain injury can vary dramatically from person to person and the part of the brain effected.
"My husband has brain injury in the right hemisphere says the neurologist, what will be the impact?" Read more ...
"My mother can not talk due to braindamage in the left hemisphere. What are other consequences to be expected?" Read about left and right brain damage, damage to the little brain (cerebellum) .. Read more ...
Take a 3D Brain tour: (two different tours)
Learn more about the different lobes and what a damage in that area means: