Brain tumor, cancer
Note! The information on brain tumors on this page is intended to supplement a discussion with your doctor. This general information cannot consistently uphold to any individual situation. It is rather meant to get familiar with terminology on this subject.
See our disclaimer at the bottom of the site.
A tumor, also known as a neoplasm, is a growth that develops due to uncontrolled cell division, meaning when body cells begin to proliferate uncontrollably.
Generally speaking, a tumor refers to abnormal new tissue formation somewhere in the body.
This can be benign or malignant.
A tumor is malignant when it spreads to other parts of the body.
A brain abscess, a cavity filled with bacteria (or fungi) and pus, causes the same symptoms as a brain tumor but is not brain cancer. With a brain abscess, inflammatory markers in the blood are elevated, which quickly provides clarity.
A brain cyst is a fluid-filled cavity in the brain.
This can be inflammatory fluid, but it is also not a tumor.
Compressed Brain Tissue
With a brain tumor, the distinction between benign and malignant is not very important. A benign tumor, like a malignant tumor, takes up space within the skull, compressing brain tissue and causing increased pressure. This process is also called increased intracranial pressure.
 brain tumor on scan
brain tumor on scan
Primary and Secondary brain tumors
Tumors are generally separated into two categories:
- A primary brain tumor is a tumor that started within the brain tissue, for example a tumor in the meninges , cells of the braintissue, or in the pituitary gland. See the more extensive page on primary brain tumor.
- A secondary brain tumor is a metastasis (metastatic) cancer that has spread from different areas of the body, for example: a breast, the lungs or a melanoma (skin cancer). They are known as brain metastasis tumors. Metastatic brain tumors are more common than primary brain tumors, with about half of the metastases originate from lung cancer.
The problem with brain tumors is that both the tumor and the treatment may damage the brain.
Radiation therapy, surgical removal of the tumor and/or drug therapy all disrupt the brain's complex network.
Motor skills, speech, vision, and/or cognitive functions may deteriorate as a result of the treatments.
Grades 1-4
A tumor is classified into four grades.
- Grade I: This is a tumor that behaves virtually identically to normal brain tissue.
- Grade II: This type of tumor shows increased growth of glia (brain cells that supply neurons), but without any signs of malignancy.
Grades I and II are considered single-grade astrocytomas.
- Grade III. This indicates malignancy. Changes in the cell nuclei and increased blood vessel growth occur.
- Grade IV. This type involves an uncontrolled tumor that spreads rapidly. The blood vessels can no longer keep up, and tissue destruction occurs.
However, the grade doesn't tell the whole story, as tumor behavior may vary from person to person.
A person may change...
A brain tumor may affect the affected person's character, behavior, and cognitive functions.
This is not only caused by uncertainty and stress, but may also be caused by the tumor's location in the brain. Therefore, personality changes may also have a physical cause. Certain character traits may be strengthened, but other, new behaviors may also occur.
Cognitive changes occurred in 90% of people with a brain tumor or brain metastasis (spread to the brain), or with treatment for the tumor or metastasis. This was the case with surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy.
Memory, attention, concentration, and the pace of thinking and acting may be affected. A person may become hyperactive, but also apathetic. Some people become suspicious or have difficulty with executive tasks.
A common complaint, however, is fatigue. Some call this a sudden feeling of exhaustion because their energy levels are short during the day.
Symptoms may vary
A brain tumor may cause a wide variety of symptoms, which depend on the location and size of the tumor and/or damage from radiation and/or chemotherapy.
Because symptoms may progress gradually, people sometimes don't always attribute these slow changes to the brain tumor.
Be aware of this!
Possible symptoms
Different brain tumors may give very different symptoms. The symptoms are dependent on the location and the size of the tumor.
- headache (although headaches often only occur in a later stage when the pain is pressing against something, as the brain itself is numb. Pain is felt on the outside of the head: skull, meninges, muscles, and blood vessels)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Vomiting without nausea
- Paralysis
- Epilepsy
- Seizures
- Drowsiness
- Hearing and visual disturbances
- Misfunctions such as speech problems, unsteady gait, and partial paralysis, depending on the location of the tumor in the head. If the tumor grows in a part of the brain that controls movement, paralysis may occur in the other side of the body
- Sometimes with slow-growing tumors, behavioral changes may occur: lethargy, apathy, or agitated behavior, aggression, and rapid changes in behavior
- Cognitive changes
- Severe fatigue, the daily energy supply is depleted more quickly
- Day-night shift/ the day-night rhythm is reversed
- Memory problems
Depending on the location of the tumor, the consequences may include the following:
- unrestrained emotions
- aphasia difficulty or inability to speak, halting speech dysarthria,
slower speech - apraxia (inability to perform complex actions in sequence)
- neglect
- problems with swallowing, dysfagia
- visual problems
- weakness in arm or leg/paralysis
- difficulty with balance
- hemianopia (loosing half of the visual field)

Tumor in the left hemisphere
-
(smaller) paralysis
-
problems with language, such as not pronouncing words correctly or unable to understand what others say.
-
there may be memory disorders, for more see information on our page on damage in left hemispere
Tumor in the front of the brain
- behavioral changes may occur, such as inertia and indifference or even irritability and moodiness. Impulsivity but also lack of initiative
Tumor in the back of the brain
- sometimes causes problems with reading and seeing, see our page on occipital lobes
Tumor in the pituitary gland
- may give eating disorders, see our page on this
Tumor in the brainstem
- may cause drowsiness and fatigue, see our page on brainstem
Brain damage caused by surgery and/or chemotherapy
Brain damage caused by surgery and/or chemotherapy is discussed on a dedicated page.
About 30% of people who undergo chemotherapy continue to experience cognitive problems.
Read more by following this link.
Types of primary brain tumors
- gliomas, tumor of the brain tissue
- meningiomas, a tumor in the meninges, the most common primary tumor
- Adenoma, Craniopharyngioma, pituitary tumor
- Angioma, tumor in the blood vessels
- metastases
- tumors in or near the spinal cord
- vestibular schwannoma, often called an acoustic neuroma
- medulloblastomas
- Brainstem glioma / pontine glioma
- Plexus tumors
- Pineal parenchymal tumors Grade II + III
- Pineoblastoma / pinealoblastoma Grade IV
- Papillary tumor Grade II + III
- Low-grade gliomas
- Germ cell tumor
- Germ cell tumors of the pineal gland
- Medulloblastoma
- Brain metastases
- Pituitary tumors
- Rare tumors
Click here for Subpage on primary tumors
Treatment of a tumor
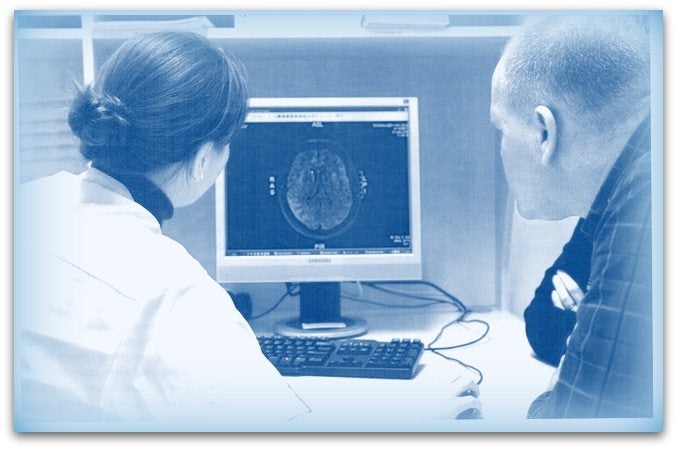
A neurologist makes the diagnosis on the basis of the symptoms.
An additional CT or MRI scan may show the tumor in the brain.
The treatment depends on the type of tumor and the stage in which it is located.
The tumor is located in the middle of healthy tissue, making it sometimes difficult to remove surgically.
A radiation treatment or chemotherapy (drugs) can then prevent a cancer comes back again.
The future expectation of someone with a brain tumor varies from situation to situation, from human to human.
MRI examination
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (NMRI), or magnetic resonance tomography (MRT) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology with a very strong magnet which can create images with sound waves of someone's head (in this case).
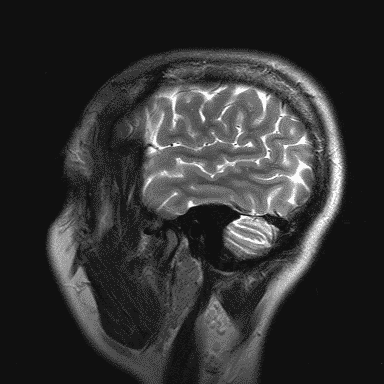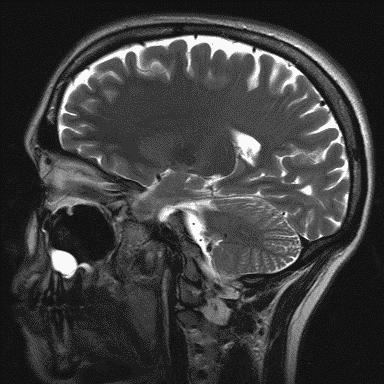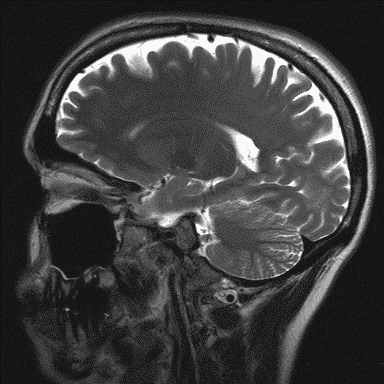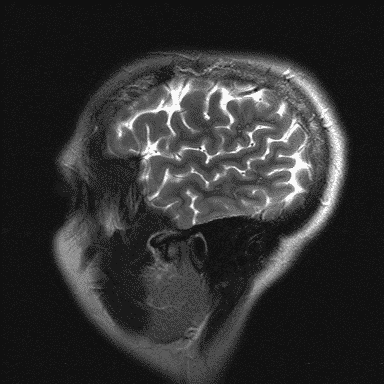
MRI is the investigative tool of choice for neurological cancers as it is more sensitive than CT for small tumors. The contrast provided between grey and white matter makes it the optimal choice for many conditions of the central nervous system.
Because it is a very strong magnet patients are requested to remove all (ferromagnetic) metallic objects, often by changing into a gown or scrubs. Also ferromagnetic metal in the body like cochlear implants and most permanent pacemakers are, for safety reasons, not allowed.
The appliance makes a lot of noise.
They give a bell in your hand and there is a microphone in case you want to talk to the employee.
You are allowed bring your own music to listen to.
Read the explanation on all brain scans via this link.

Ependymoma in children and young adults
An ependymoma is a malignant brain tumor that originates in the ependymal cells. These brain cells line the inside of the brain's ventricles and the central canal of the spinal cord.
Therefore, ependymomas also occur in the spinal cord.
This brain tumor occurs in 1 in 400,000 children. Patients are usually young. A third are under two years of age.
Ependymomas in the spinal cord are more common in adolescents and young adults.
Pseudotumor cerebri (PTC) Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension
With a pseudotumor cerebri the patient experiences symptoms of a brain tumor even though there is no tumor present.
The term 'pseudotumor cerebri' is outdated. The condition is now known as Intracranial Hypertension (IH or IIH) or Benign Intracranial Hypertension (BIH).
It is an unusual condition characterized by an unexplained buildup of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain.
The affected person experiences almost all the symptoms of a brain tumor, but not tumor is present. Symptoms may include headache, pain in the neck and/or shoulders, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), nausea, vomiting, blurred vision, and sometimes double vision.
This condition should not be confused with hydrocephalus, which involves excess cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles of the brain.
It can be caused by, among other things, Cushing's disease.
advertisements are not ours
Resources
Hersenletsel-uitleg.nl: https://www.hersenletsel-uitleg.nl/soorten-hersenletsel-hersenaandoeningen/hersenletsel-door-een-tumor
ziekenhuis.nl
nederlandse vereniging voor neurochirurgie
Voorlichtingscentrum van de Nederlandse Kankerbestrijding
epilepsie vereniging
Vereniging van neurologen,
IntegraleKankercentra,
www.hersentumor.nl/ouders-en-kinderen,
www.pseudotumorcerebri.nl
Cerebraal, Jenny Palm
Cognitief wetenschapper Michiel de Ruiter (AMC en NKI-AvL) AMC Magazine. Elske van Riel / KWF/ www.nfk.nl en neuroradioloog Liesbeth Reneman van het AMC. Het wetenschappelijk blad 'Human Brain Mapping